Central Sleep Apnea (CSA)
Central sleep apnea is a breathing disorder in which breathing interruptions during sleep occur because the brain temporarily stops sending signals to the respiratory muscles. This is in contrast to obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), where the breathing obstruction is physically caused by a blockage of the airways.
Characteristics of Central Sleep Apnea
In central sleep apnea, the cause of breathing problems lies in a failure of respiratory regulation in the brain, meaning there is no physical airway obstruction as seen in OSA.
CSA can occur without an increase in carbon dioxide levels in the blood (normocapnic CSA). However, in some cases, there is an elevated concentration of carbon dioxide (hypercapnic CSA).
The Center for Sleep Medicine at Kempenhaeghe offers a specialized and multidisciplinary approach to the diagnosis and treatment of central sleep apnea. We aim for a personalized treatment plan to manage breathing disorders during sleep and improve the patient's quality of life.
Diagnosis of Central Sleep Apnea
The diagnosis of CSA at the Center for Sleep Medicine often includes the following examinations:
- Polysomnography (PSG): A comprehensive sleep study that continuously records brain activity, breathing, and other physiological signals. This helps determine whether the breathing problems are of central origin.
- Esophageal pressure measurement and transcutaneous CO2 monitoring: In some cases of CSA, esophageal pressure and blood carbon dioxide levels are measured to accurately diagnose the severity and cause of the breathing disorder.
Treatment of Central Sleep Apnea
The treatment of CSA at the Center for Sleep Medicine follows a step-by-step approach and depends on the severity of the condition. Possible treatment options include:
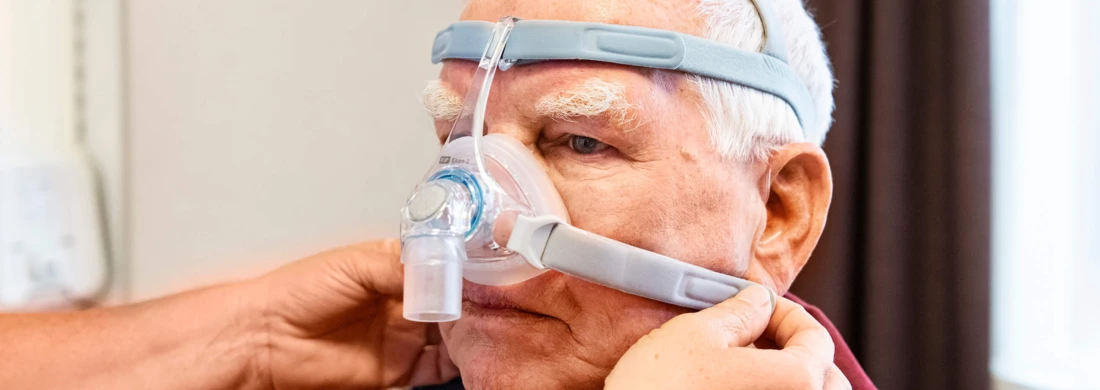
- CPAP therapy (Continuous Positive Airway Pressure): Often the first step in treating CSA, CPAP keeps the airways open by continuously delivering pressurized air, which can help stabilize breathing.
- Oxygen therapy: Some patients receive supplemental oxygen to support breathing during sleep.
- Acetazolamide: This medication may be prescribed to improve breathing patterns.
- Adaptive Servo Ventilation (ASV): If other treatments prove ineffective, ASV can be used. This device dynamically adjusts to the patient’s breathing needs and provides the most advanced support for CSA.
Central Sleep Apnea in Normocapnic and Hypercapnic Patients
- Normocapnic CSA: Patients with normocapnic CSA, where carbon dioxide levels in the blood remain normal, can often be treated with CPAP or ASV.
- Hypercapnic CSA: If there is an increased carbon dioxide level (hypercapnia), referral to a home ventilation center may be necessary for more intensive care.
CSA in Special Populations
CSA can also occur in individuals with intellectual disabilities. We provide specialized care with adapted diagnostic and treatment methods tailored to this group.